DECOMPRESSION THEORY
HISTORY : J.S. HALDEAN
discover it in the 1900s
Henry’s law is applied
to this theory (gas absorption)
Theoretical tissues
: tissue of the body (bones, blood,
liver, heart, fat, lungs, etc…)
Half-live / half time
: the time that a tissue absorb N2 until it’s half full
M-value : maximum
amount of N2 in one tissue
Haldean works with 5
theoretical tissues and the biggest tissue is 75’
US. Navy table (SSI)
with 7 theoretical tissues and the biggest tissue is 120’
Padi Tables with 14
theoretical tissues and the biggest tissue is 60’
The US Navy table have
been tune-up with Doppler machine to count the silent bubbles in the body after
a dive
The Doppler limit (or
NDL) is the maximum time that we can stay underwater until the inside PPN2
equal the outside PPN2
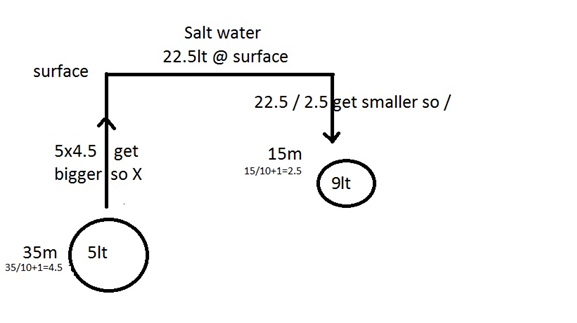
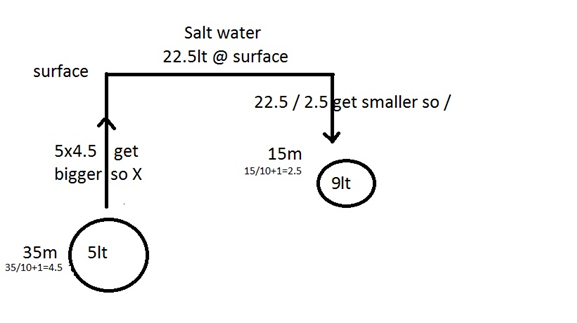
Exemple:
Meters pressure in bar percentage partial
pressure
21%02 0.21ppo2
0 1 +79&N2 +0.79ppn2
--------- ------------
100% 1 bar
21%o2 0.42ppo2
10 2 79%n2 1.58ppn2
--------- ------------
100% 2 bar
The NDL at 10m is 160
minutes , so after this amount of time, the body is saturated with N2 and we
need to ascent otherwise we pass in decompression dive
DIVE COMPUTERS:
Dive computers gives
more time underwater because they recalculate the NDL all the time
But on the 1st
dive, dive computer and dive table give the same amount for a given depth.
The same roles apply
to dive computers and tables:
- never share a computer
- never plan to the NDL time
- ascent max 9m/ minute
- if computer fail during a dive, ascent to
5m and stay there as long as your air supply permit and don’t dive for
24hours
- safety stop at 5m for min 3 minutes
- always begin with the deepest dive and
work shallower
- don’t do up down up down dives
- adjust if you dive in altitude (more that
300m)
- wait 18-24 hours after a dive to ascent in
altitude (more than 300m) or before taking a pressurized plane
- 24 hours if taking non pressurized plane
or ascending higher than 2’400m altitude
Computers allow multilevel
diving.
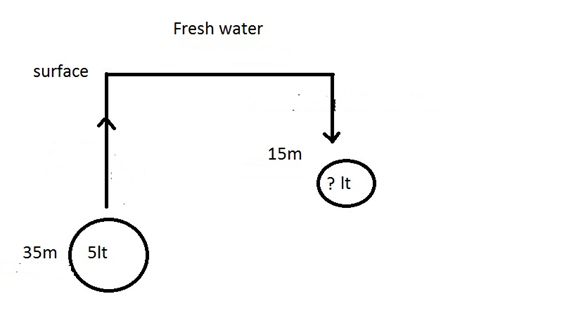
ALTITUDE DIVING
- Diving in altitude (more than 300m )
required special procedures since the atmospheric pressure is less than at
the sea level and we dive in fresh water
- when diving in altitude, you need to know
your altitude to convert the real depth to theoretical depth, the
capillary gauge do it automatically
- at 5.500m the atmospheric pressure is ½ so
0.5 bar



.jpeg)